"Cortisol (hydrocortisone) is a steroid hormone, or glucocorticoid, produced by the adrenal gland.[1] It is 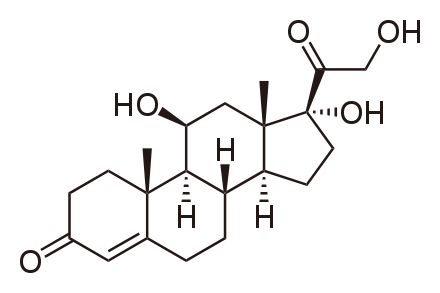 released in response to stress and a low level of blood glucocorticoids. Its primary functions are to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis; suppress the immune system; and aid in fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism.[2] It also decreases bone formation. During pregnancy, increased production of cortisol between weeks 30-32 initiates production of fetal lung surfactant to promote maturation of the lungs. Various synthetic forms of cortisol are used to treat a variety of diseases."
released in response to stress and a low level of blood glucocorticoids. Its primary functions are to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis; suppress the immune system; and aid in fat, protein and carbohydrate metabolism.[2] It also decreases bone formation. During pregnancy, increased production of cortisol between weeks 30-32 initiates production of fetal lung surfactant to promote maturation of the lungs. Various synthetic forms of cortisol are used to treat a variety of diseases."
"Cortisol is produced by the adrenal gland in the zona fasciculata, the second of three layers comprising the outer adrenal cortex. This release is controlled by the hypothalamus, a part of the brain. The secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) by the hypothalamus triggers anterior pituitary secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH is carried by the blood to the adrenal cortex, where it triggers glucocorticoid secretion."